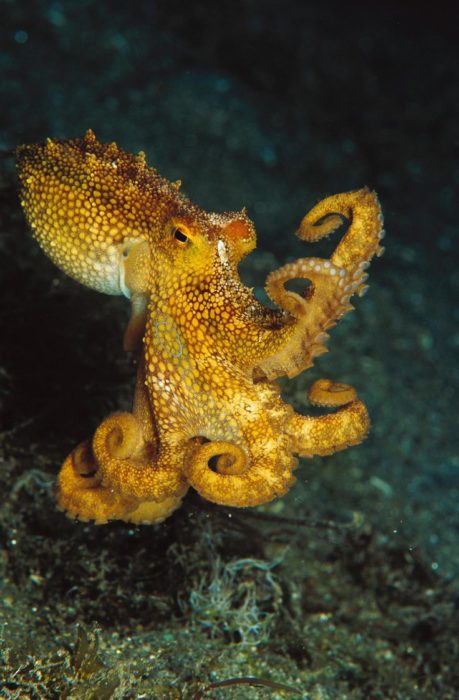
Have you ever wondered what would happen to an octopus on ecstasy? If you have, then you aren’t alone. Gul Dolen, a neuroscientist a Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, had wondered the same thing.
She and Eric Edsinger, conducted a study on the effects of the drug ecstasy, also known as (+/−)-3,4-methylendioxymethamphetamine or MDMA, on the brains and behaviors of octopuses. They placed octopuses a chamber and allowed them to explore on their own. The chamber was connected to two others, one containing a hidden octopus and another containing a strange object. They then compared the time the octopus spent with either the object or the second octopus. The octopus tended to gravitate toward the other animal but only if it was a female. If the second octopus was a male, it avoided the second creature. This was true for bothe male and female octopuses placed into the chamber.
Then they gave the octopus a hit of MDMA, by dunking it into a solution containing the drug to allow it to soak in through its gills. While on the drug they spent way more time with male octopus. Describing their behavior, Dolen says”
“They mashed themselves against one wall, very slowly extended one arm, touched the [other animal], and went back to the other side. But when they had MDMA, they had this very relaxed posture. They floated around, they wrapped their arms around the chamber, and they interacted with the other octopus in a much more fluid and generous way. They even exposed their [underside], where their mouth is, which is not something octopuses usually do.”
This was very unusual behavior for octopuses, which are known to live in solitude. MDMA appeared to make the animals more social in a way that mimics its effects in humans. After studying serotonin transporter proteins in humans and octopuses, the researchers found that the sequences had a 50% match. It is especially similar in the part of the protein where MDMA binds, and that is why they believe they see similar effects in behavior.
But, some scientists remain unconvinced. The researchers always administered the drug after the control, so their more exploratory behavior could just be due to them being more comfortable in their surroundings. Other scientists suggest that ecstasy may just be interfering with the animal’s ability to detect chemical information from potential mates.